polarimeter for sugar analysis|how to measure polarimetry : private label Calculate the specific rotation of sugars using a polarimeter. Identify common sugars and artificial sweeteners in everyday beverages. Resultado da 16 horas atrás · Giá vàng trong nước hôm nay 1/3/2024. Đầu giờ sáng 1/3, giá vàng 9999 của SJC tăng 100 nghìn đồng/lượng ở cả chiều mua vào và .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Crefisa. Empréstimo pessoal para negativados. . A Crefisa t.
Calculate the specific rotation of sugars using a polarimeter. Identify common sugars and artificial sweeteners in everyday beverages.Polarimetry, using a flow-through polarimeter at 589 nm, is the general method of sucrose analysis in bulk raw and white sugars. Traditional polarimeters are being replacing by .A polarimeter is a device for determining the polarisation direction of the light or the rotation of an optically active substance. . Examples of optically active media are sugar, lactic acid and quartz. . highly selective and offer mainly very fast measurements in many areas of analysis. Polarimeters measures the angle of rotation of .Polarimetry of sugar solutions Polarimetry is frequently used for determining the quality of sugar products. Measurements are made by polarimeters or saccharimeters with the scale in angle degrees (0) and sugar degrees ( Z). Angle of rotation depends linearly on concentration of sugar in the solution other parameters (temperature, light source,
7.3. Methods of Analysis. A large number of analytical techniques have been developed to measure the total concentration and type of carbohydrates present in foods (see Food Analysis by Nielssen or Food Analysis by Pomeranz and Meloan for more details). The carbohydrate content of a food can be determined by calculating the percent remaining . So in layman’s terms, a Saccharimeter can be said to be a “sugar polarimeter”. The International Sugar Scale (°Z) . (International Commission for Uniform Methods of Sugar Analysis) as 26 grams sucrose per 100 cm 3.When measured using the wavelength 546.44nm (mercury isotope 198) a normal sucrose solution has an optical rotation of 40. .
Rudolph Research Analytical 55 Newburgh Road Hackettstown, NJ, 07840 USA Phone: 973-584-1558 Fax: 973-584-5440 [email protected], using a flow-through polarimeter at 589 nm, is the general method of sucrose analysis in bulk raw and white sugars. Traditional polarimeters are being replacing by polarimeters using light of longer wavelengths, λ =880 nm, which can be used for monitoring a colored (through not a turbid) solution, and so decreases solid waste .
polarimetry techniques
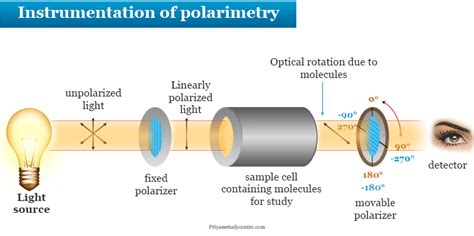
Density of Sugar solution. Concentration of the solution. Temperature of the solution; Wavelength of the light employed; Laurentz Polarimeter. Laurentz Polarimeter is the simplest form of Polarimeter and consists of two Nichol prisms known as Polarizer (P) and Analyzer (A).Polarimetry, using a flow-through polarimeter at 589 nm, is the general method of sucrose analysis in bulk raw and white sugars. Traditional polarimeters are being replacing by polarimeters using light of longer wavelengths, λ =880 nm, which can be used for monitoring a colored (through not a turbid) solution, and so decreases solid waste .listening while commuting or multitasking. Sugar Identification Using Polarimetry sugar and greatly alter the polarimetry. This work studies the effect of amino acids such as glycine and L-alanine on the optical rotation of aqueous dextrose and sucrose. Sugar Identification Using Polarimetry ANALYSIS. FOR REFINERIES, SUGAR-HOUSES, EXPERIMENTAL .
Polarimetry, in analytic chemistry, measurement of the angle of rotation of the plane of polarized light (that is, a beam of light in which the vibrations of the electromagnetic waves are confined to one plane) that results upon its passage through certain transparent materials. . Polarimetric analysis is commonly used in the sugar industry .
Principles of Polarimetry. Polarimetry measures the rotation of polarized light as it passes through an optically active fluid. The measured rotation can be used to calculate the value of solution concentrations; especially substances such as sugars, peptides and volatile oils. A polarimeter consists of a polarized light source, an analyzer, a graduated circle to measure . Blank: Take water as blank and bring the temperature to 25°C and fill Polarimeter tube. With Blank take five readings of the solution. Clean the Polarimeter tube and fill with the sample solution. Take five readings at 25°C. Calculation Correction of rotation = Av. Observed reading - Av. Blank reading 100 µ x 100the polarimeter. Tilt the cell so that any remaining bubbles are caught in the Bubble Catch, which is the fat part of the cell. 3. Open the file named Polarimeter Introduction. 4. Start recording data. It is important to collect data for the peak closest to zero. Move the analyzer by rotating the wheel so that the peak closest to zero is collected.This notation means that the measurement was conducted at 25 o C using the D-line of the sodium lamp (λ=589.3 nm). A sample containing 1.00 g/mL of the compound in a 1 dm tube exhibits an optical rotation of 3.5 o in clockwise direction. Note that the instrument used in Chem 30BL and Chem 30CL can provide the specific optical rotation, which already corrects the .
Polarimetry is an instrumental analytical technique that uses rotation of polarized light (i.e. optical activity) by some substances as a measure of their concentration in a solution or other properties. The instrument used to measure optical activity is called a polarimeter. When the same is used for measuring quality of sugar the nameAtago Portable Refractometer Polarimeter for Sugar Analysis.Angle of Rotation, Brix (%), International Sugar Scale, Temperature.The RePo-1 is a refractometer and polarimeter hybrid unit. With as little as 3mL sample, the RePo-1 can measure both brix and optical rotation of the sample. With the press of a button, Brix, Angle of Rotation, International Sugar Scale, Purity, .Sugar Concentration through Polarimetry. Students use a polarimeter to determine the unknown concentration of a sucrose solution. Grade Level: College. Subject: Chemistry. Student Files. Sugar Concentration through Polarimetry: 477.29 KB: Teacher Files. Sign In to your PASCO account to access teacher files and sample data.
This angle of rotation can be determined by a polarimeter with the highest possible precision. Analysis of active sugar solutions, and of any active solutions, is the most important application of polarimeters in the quality control, determination of concentration, and purity control in food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries. Ellipsometer The optical activity of a substance is measured by its specific rotation (or specific rotatory power).. The specific rotation of sugar solution is determined by the formula;. S = θ / LC. where ‘θ’ is the rotation produced in degree, L is the length of the tube in the decimeter (1 decimeter = 10 cm) and C is the concentration of the active substance in gm/cc in the solution.Polarimetry can be defined as the analysis of the rotation of polarized light by transparent components. Polarimetry is a sensitive and non-destructive . It is used to assure product quality by determining the purity and concentration of compounds in sugar foods, syrups and cereals. Polarimeter applications consist of the quantitative and .
First-class sugar analyzer for high-precision analysis of products in the sugar industry – simple, precise, quick. . Your investment in a MCP sugar polarimeter is secure and sustainable, no matter which kind of sample clarification you are using today or in the future. MCP Sucromat models can be purchased as dual-wavelength instruments or .
All types of sugar are chiral and therefore optically active. Sucrose has a specific rotation angle of +66.4°, glucose +52.7° and fructose -92°. Sugar solutions are not stable and quickly break down into their components. The sugar purity analysis is carried out with a combination of polarimeter and refractometer from SCHMIDT + HAENSCH.
Sugar industry: Polarimetry is used in the sugar industry to measure the sugar content of fruit juices, which is important for quality control and to ensure that the juice has the desired sweetness. . Data analysis and interpretation: The data should be analyzed carefully, and the results should be interpreted correctly. It is important to .founded in 1897, publishes detailed laboratory procedures for the analysis of sugar. The following methods are based on the use of a polarimeter. GS1/2/3/9-1 (2011) Determination of Polarisation of Raw Sugar - Official Method GS1/2/3-2 (2005) Polarisation of Raw Sugar without Wet Lead Clarification - Tentative MethodICUMSA Methods of Sugar Analysis presents the recommendations of the International Commission for Uniform Methods of Sugar Analysis (ICUMSA) that are based on thorough investigations of methods likely to prove practical and appropriate for the sugar industry. This book discusses the procedures for raw sugar polarization.
@EasyScience_NTU_041 #Physics_experiments #PolarimeterTitle: PolarimeteryTask: Optical rotation of given solution. 2- Specific rotation of given solut. In this article, we demonstrate the potential application of polarimetry and fluorescence spectroscopy for classifying mono and disaccharides (sugar) both qualitatively and quantitatively. A phase lock-in rotating analyzer (PLRA) polarimeter has been designed and developed for real time quantification of sugar concentration in a solution.
polarimetry science
karl fischer titration coulometric volumetric distributor
polarimetry practices
Resultado da 19 de dez. de 2021 · When Billie Eilish said this week that viewing pornography at a young age had “devastated” her, 19-year-old Jay .
polarimeter for sugar analysis|how to measure polarimetry